Neutral earthing is a system for protecting property and people that defines a path through which an electrical fault will flow.
When a fault occurs on the electrical distribution network, it takes the shortest and most conductive route: it is therefore crucial to install this type of protection so that the fault does not spread to the user (and vice versa).
Thanks to the neutral earthing system, the fault will trigger the various protective devices installed on the electrical system, before flowing into the ground at the location specified by the electricity company.
The different neutral conductor systems
There are 3 neutral systems, which differ according to the connections made between the neutral, the earth and the metallic grounds.
A metallic earth is a conductive part of electrical equipment that is not under voltage in an electrical system, but which may become so when a fault occurs, and thus become dangerous to humans.
These systems are named by two letters: the first refers to the type of connection at the distribution substation. The second refers to the type of connection at the user’s premises.
- T : Connected to earth
- N : Connected to neutral
- I : Isolated from earth
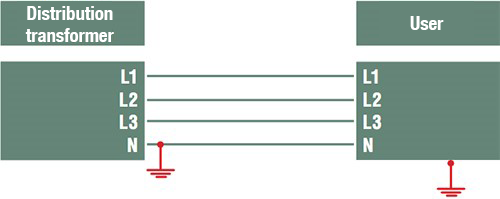
The TT system
The neutral and metallic grounds are earthed at the distribution substation and at the user’s premises.
The TN system
The neutral is connected to earth at the distribution substation, while the user is connected to the neutral. There are two types of configuration under this system:
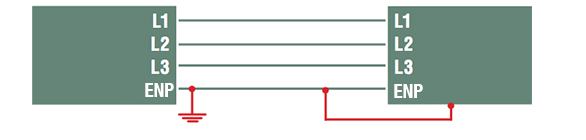
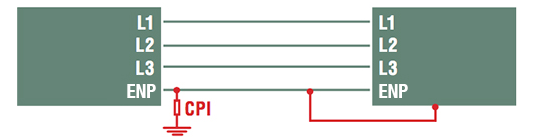
- TN-C : the neutral merges with the protective conductor. It therefore no longer performs its neutral function alone and is renamed “ENP”, which stands for Electrical and Neutral Protection.
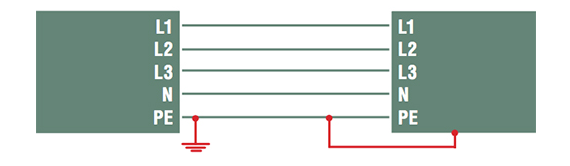
- TN-S : the neutral and the protective conductor are separated. The metallic grounds are connected to earth but also to neutral at the same point, at the distribution substation.
The IT system
The neutral conductor is connected to earth via a special device that prevents the electricity supply from being cut off when the first fault occurs. However, the power will be cut off when a second fault occurs. On the user’s side, the metal grounds are earthed.
Earthing the neutral conductor on overhead power lines
These different systems have different applications and costs. Depending on the configuration of the site and the budget allocated to the installation, a certain system will be preferred over another.
Which neutral earthing system should I choose?
The TT system is the most widespread on overhead power lines: it is simple to implement, while remaining an economical and effective solution.
The TNS system is a little safer than the TT system, since it separates the neutral from the protection, thus avoiding excessive sensitivity to faults. However, this neutral earthing system is more expensive.
The IT system is reserved for large consumers such as industrial companies. It is also used for connecting hospitals, as it avoids the first power cut. However, this system is more complex to implement and requires a permanent human presence on site.
How is the neutral connected to earth?
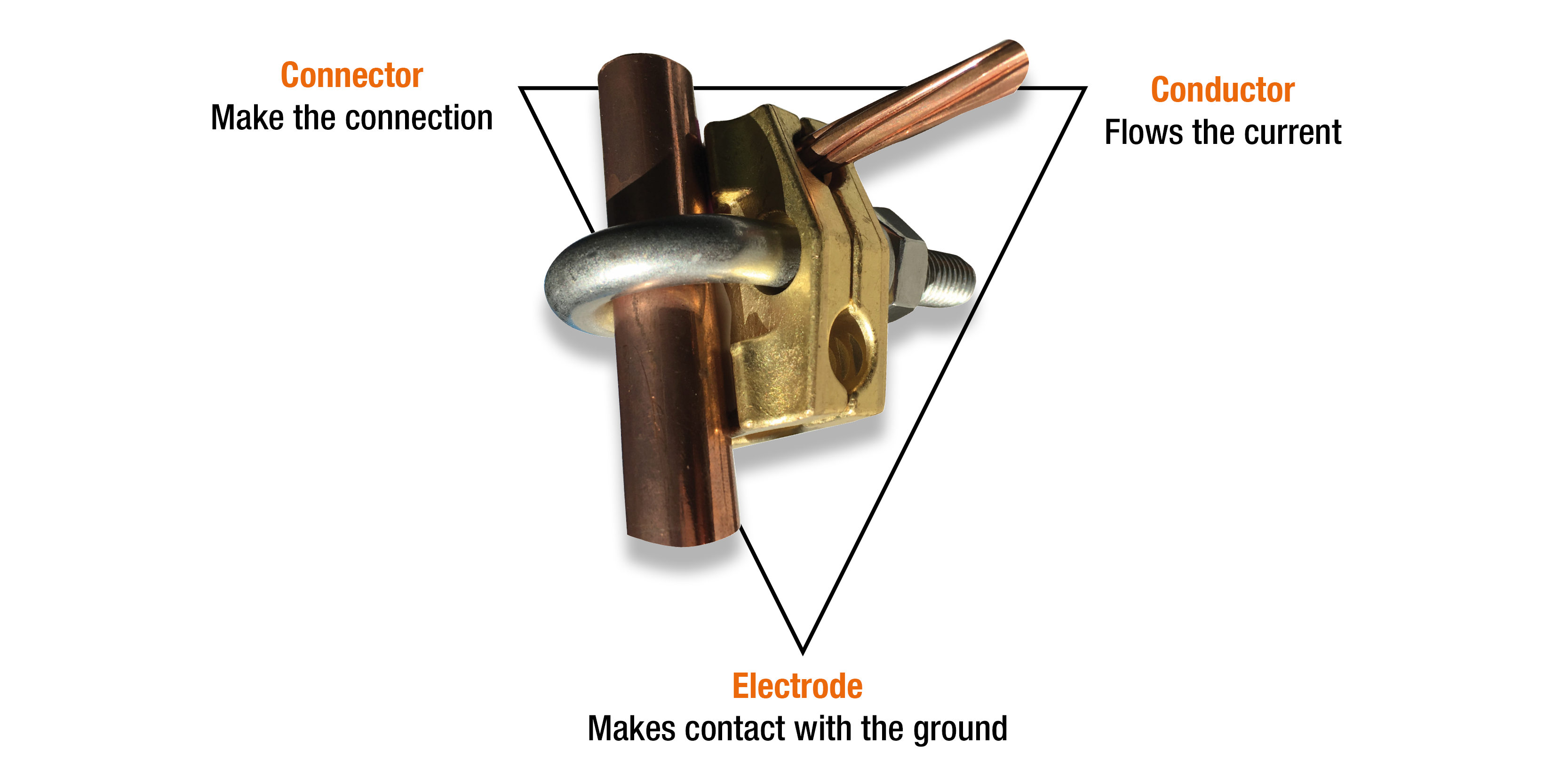
An electrical installation is earthed by means of an earth connection or an earth circuit. The earthing system connects the installation to the ground, allowing the fault to drain into it. The earthing system has three main components.
Contact us for assistance in ensuring that your installation is safe and durable!