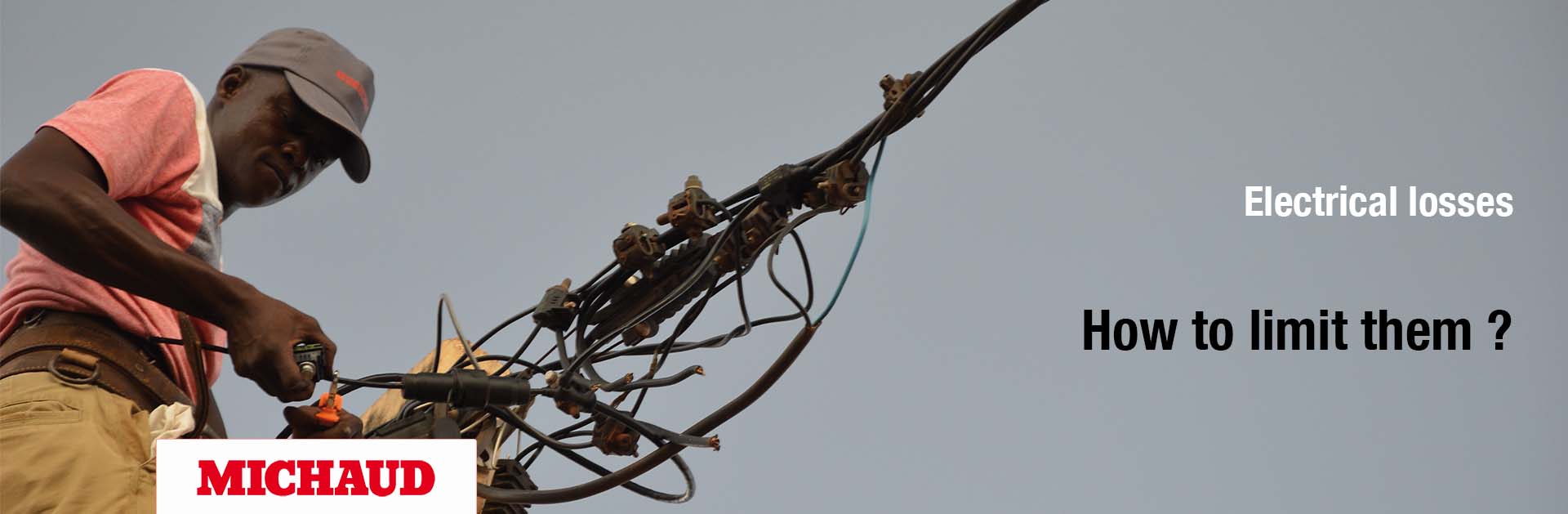
Electrical losses are the difference between the volume of electricity generated (wind power, photovoltaic, power plant…) and the volume consumed by customers.
There are two categories of losses:
– Technical losses, whose are inevitable because they depend of the transmission and distribution networks’ structure.
– Non-technical losses, whose relate to consumed but unregistered energy.
They arise from defect, failure and energy metering fraud.
Producers and distributors are very concerned by electrical losses: they have to limit them because they have to predict the purchase of the volume of electricity needed by consumers.
These losses have a cost which is absorbed by grid system operator. Frequently, they pass the price on the consumers’ bills.
There are big differences between countries: electrical losses represent approximately 7% for OECD’s countries and 20% for some others. It can question the viability of a company’s business model.
We can observe how important is the identification of electrical losses in order to deploy actions to reduce them. Let’s discover their specificities.
Technical losses: understand the physical phenomena to optimize electrical networks
Technical losses are due to transmission and distribution of electricity.
The various types of technical losses
Joule’s law: “the conversion of electric energy into heat energy by the resistance in a circuit. » (Source: Britannica.com). Losses are bigger if the density of electric current is high.
Corona discharge:“A corona discharge is an electrical discharge possible because of the ionization of air surrounding a conductor that is electrically charged.” (Source: Georges Wypych, Handbook of Adhesion Promoters). This phenomenon occurs on high voltage power lines.
Iron losses:“It is the power dissipated in the magnetic core subjected to a time varying magnetizing force. They are constant for a given applied voltage and unaffected by the load on the transformer.” (Source : Classical and Recent Aspects of Power System Optimization, S. Tamil Selvi, … S. Rajasekar).
How to reduce technical losses?
These losses come from natural phenomena and are unavoidable.
Adapting the architecture of networks
Prefer electric transport via HV lines. It allows to limit the losses. “Losses scale with the square of a wire’s current. That square factor means a tiny jump in current can cause a big bump in losses. Keeping voltage high lets us keep current, and losses, low.” (Source: insideenergy.org)
Reduce the distance covered by power lines by favoring decentralized production.
Reduce iron losses by modernize electrical transformer
Adapt production to consumers habits to not produce electricity more than necessary. Distributors can use smart metering equipment.
The choice of materials
The distributor can limit electrical losses by modernizing networks. He has the possibility of:
- Replace unsuitable equipment
- Replace aging and deficient equipment
By implementing a new network, he can also:
- Dimensioned infrastructures properly to reduce the linear resistance of electrical conductors: high-performance alloys, adapted cable diameter etc.
Non-technical electrical losses : what can be done to avoid them ?
These losses are different from technical losses. It is the result of equipment malfunctions, metering anomalies, poor billing control or fraudulent use of energy.
Non-technical losses and lots of unpaid bills are responsible for a large part of financial losses of energy distributors.
Control measures can be taken to detect failures. Added to installation of fraud preventing equipment, a lot of electrical losses can be avoided.
Knowing and understanding these mechanisms allows to deploy the right actions to limit them. Let’s see what kind of non-technical losses can be.
The various types of non-technical losses
Technical frauds: fraudulent practices on the mechanical or electrical parts of the network and/or metering systems
Administrative frauds: refers to tariffs that do not comply with the subscribed power, billing irregularities, etc., intentional or unintentional.
These frauds cause the non-registration of a part of the electrical energy consumed.
Avoiding non-technical losses allow to distributors and consumers to save money.
Michaud develop some solutions for its clients to reduce non-technical losses by maximizing the efficiency of networks.
Anti-fraud system: an effective way to reduce non-technical losses
Thanks to a collaborative work with African and Asian national electric companies, Michaud developed an anti-fraud system. These solutions can be used in different situations: networks rehabilitation or creation of new structures.
How does it work ?
Michaud develop 5 types of equipment to protect networks from fraud.
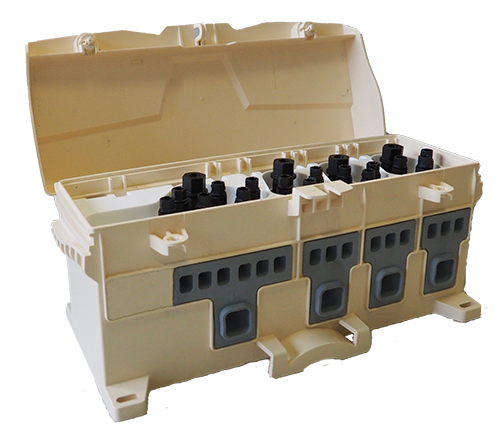

The box limits the number of connectors. Hence, the network is cleaner and fraud attempts are more visible. Moreover, connections are protected from bad weather.

The cable protects from illegal connections: conductor is inaccessible because it is surrounded by the concentric neutral. A fraud attempts will cause a short circuit.
Fuse cutout sleeve
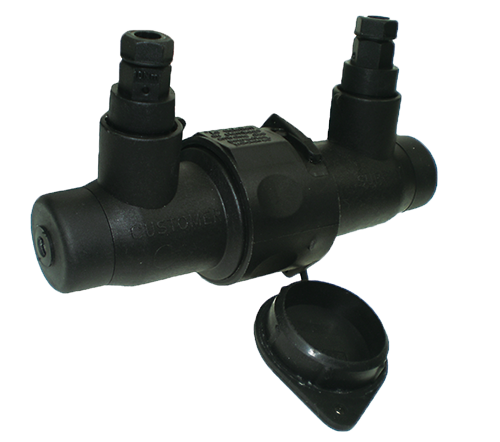

The short circuit cause by the fraud attempts burns the fuse. This system protects the line from a total short circuit. Moreover, a customer can be disconnected from the network without modification of connections and without a specific tool.
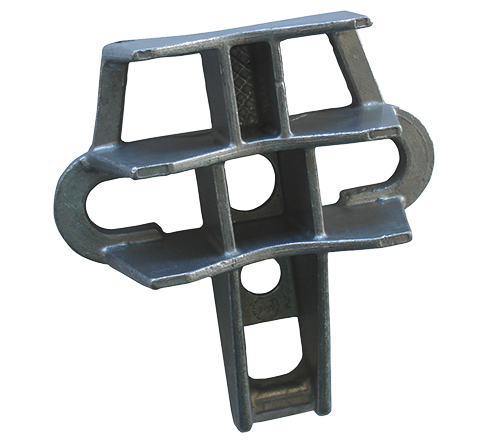
The anchoring bracket limits the number of fixings on a pole. The network is cleaner so the fraud attempts are more visible.
Fan-out kit

To realize electric connections on concentric neutral cables, Michaud develop a specific kit.
What are the challenges and benefits?
Electrical losses impact the balance sheets of distributors. To offset some of the cost, price increases are regularly applied. Those very unpopular decisions encourage development of frauds and contribute to vicious circle of non-technical losses.
Including fraud preventing in the specification during the conception of an electrical network allows to choose reliable solutions.
According to World Bank “On average, it is threefold cheaper to save 1kWh by reducing losses and improving the efficiency of the network than by investing in production means to obtain this 1kWh.”
In Cote d’Ivoire, a fraud preventing system is implemented for about ten years. The General Manager of CIE recently stated that the rate of electrical losses had dropped from 28% to 11% over the same period.
These systems allow to:
- Limit fraud attempts on live lines
- Reduce fraudulent manipulations of circuit breaker
- Protect the network against theft material for reselling
- Limit electric meters shunts
Michaud’s action
Michaud develops anti-fraud equipment for 20 years. With a large experience and exchanges with a lot of countries, we evolve our products in order to respond to the evolution of fraud practices and the increase in needs.
Senegal
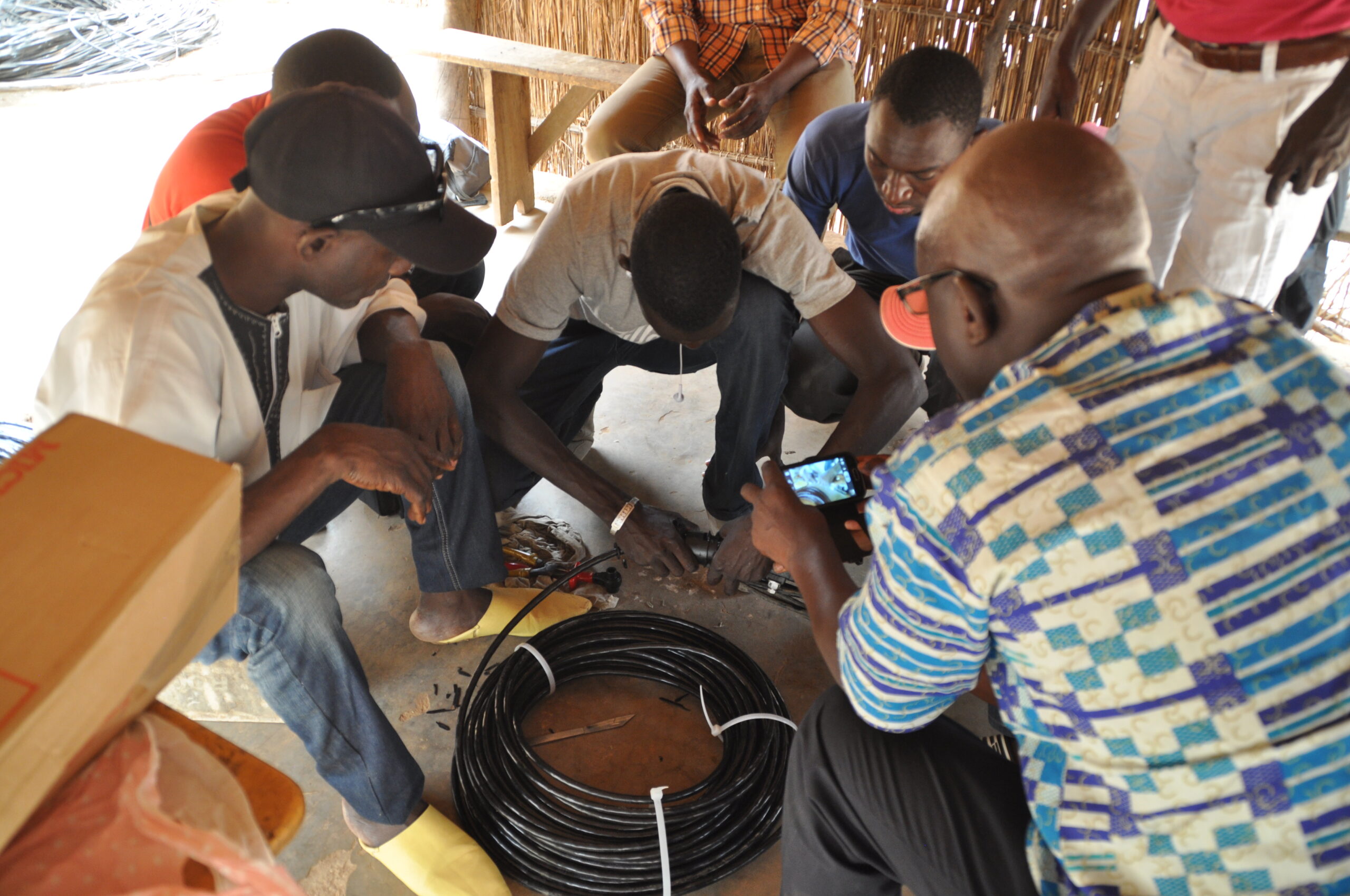
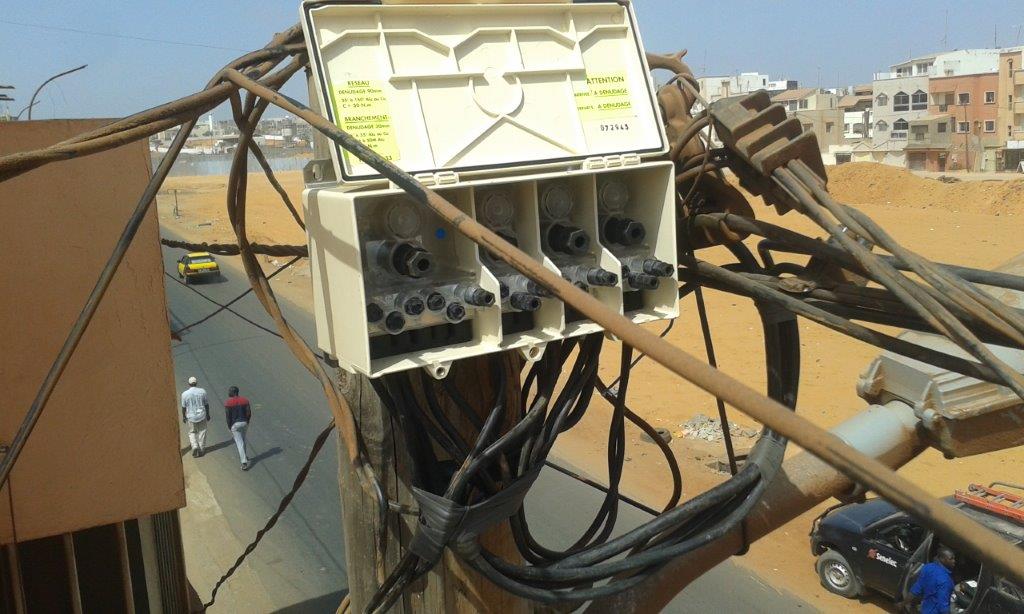
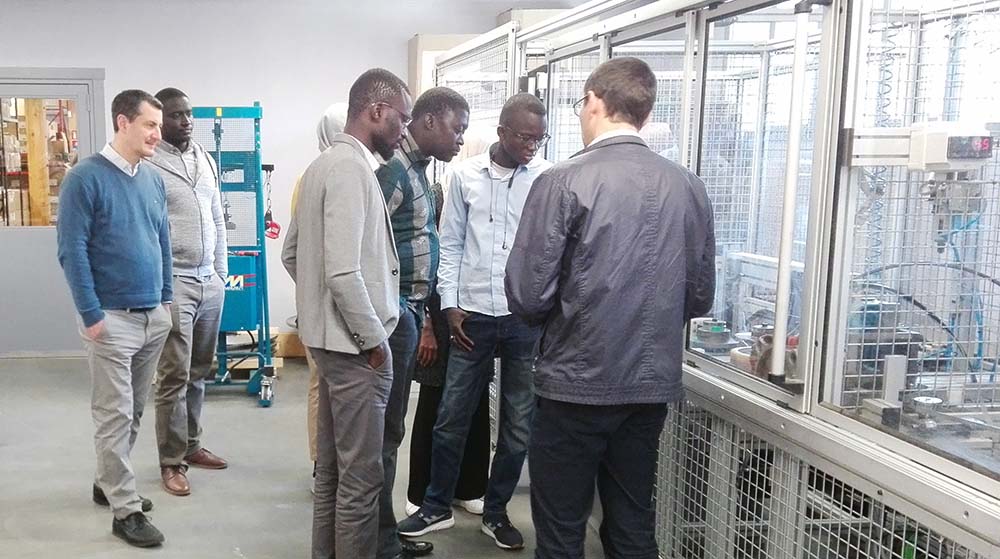



In 2017 Michaud’s team supports Senegal for the installation of multitap aerial connection box and fan-out kits.
A very successful project which ended with the visit of SENELEC to our production plant UPECA.
Togo


Michaud went to Togo to train the CEET teams for anti-fraud equipment installation. Products were successfully installed by technicians.
Cote d’Ivoire


Cote d’Ivoire also chose to use Michaud products during the installation of its anti-fraud system.



